Invasive Urology
Home > Invasive Urology
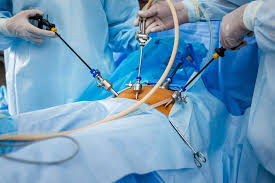
Invasive Urology
Invasive urology encompasses surgical procedures addressing disorders of the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Traditional open surgeries involve larger incisions, leading to extended recovery times. In contrast, minimally invasive techniques—such as laparoscopic, robotic-assisted, and endoscopic surgeries—utilize smaller incisions or natural orifices, reducing tissue damage and promoting faster healing. These advanced methods are employed to treat conditions like kidney stones, prostate and bladder cancers, and urinary obstructions. Benefits include reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and quicker return to daily activities. The choice between open and minimally invasive surgery depends on the specific condition and patient factors.
Know More
About Invasive Urology
-
 Symptoms
Symptoms
-
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
-
 How We Perform
How We Perform
-
 Why Is Treatment Needed?
Why Is Treatment Needed?
-
 Treatment
Treatment
-
 Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation
-
 Prevention
Prevention
Invasive urology procedures are typically considered when non-invasive treatments have been ineffective, and symptoms significantly impact quality of life. Common indications include:
Persistent Hematuria (Blood in Urine): Especially when associated with pain or weight loss.
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): That do not respond to standard antibiotic therapy.
Obstructive Uropathy: Caused by stones, tumors, or strictures leading to kidney damage.
Urinary Retention: Inability to empty the bladder completely.
Chronic Pelvic Pain: Unresponsive to conservative treatments.
Bladder Dysfunction: Such as incontinence or overactive bladder.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate invasive intervention:
Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and intravenous pyelography to visualize anatomical abnormalities.
Cystoscopy: Direct visualization of the bladder and urethra using a flexible camera.
Urodynamic Testing: Assesses bladder function and pressure.
Urine Cytology: Detects abnormal cells, potentially indicating malignancy.
Biopsy: Tissue sampling from the urinary tract for histopathological examination.
Invasive Urology focuses on surgical treatments for complex disorders of the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. These procedures often involve open or minimally invasive access to internal structures, depending on the condition and severity.
Key Points:
Anesthesia Administration:
General or regional anesthesia is used to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.Surgical Access and Technique:
Surgeons make precise incisions to access the affected organs. Procedures may be performed through open surgery, laparoscopy, or robotic-assisted techniques.Treatment Scope:
Common conditions treated include kidney stones, urinary obstructions, prostate enlargement, tumors, and structural abnormalities of the urinary tract.Preservation of Function:
Efforts are made to preserve organ function (e.g., kidneys, bladder, sexual function) while effectively treating the condition.Closure and Dressing:
Incisions are closed with sutures or staples, and sterile dressings are applied to promote healing and reduce infection risk.Post-Surgery Monitoring:
Patients are monitored for bleeding, infection, pain, and restoration of urinary function. Regular follow-up includes lab tests and imaging.Recovery Time:
Procedures may last from 1 to several hours. Most patients remain in the hospital for a few days and receive a detailed recovery plan.Outcomes:
Invasive urologic surgery often provides long-term relief from symptoms and improves overall quality of life and organ function.
Treatment in urology is essential to address conditions that affect the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Without proper intervention, these conditions can lead to serious complications, reduced quality of life, or even life-threatening outcomes.
Key Points:
Prevent Disease Progression:
Early treatment helps stop the progression of conditions like kidney disease, prostate enlargement, or cancer, preventing long-term damage.Relieve Symptoms:
Urologic conditions often cause pain, urinary problems, or discomfort. Treatment relieves symptoms such as frequent urination, burning, or blood in the urine.Restore Normal Function:
Interventions aim to restore normal function of the kidneys, bladder, urethra, or reproductive organs, improving daily living and overall health.Prevent Complications:
Untreated urologic problems can lead to infections, kidney failure, infertility, or cancer spread. Timely treatment helps prevent such complications.Improve Quality of Life:
Conditions like incontinence, erectile dysfunction, or chronic pelvic pain can severely impact life. Treatment restores comfort, confidence, and well-being.Support Fertility:
For men with reproductive concerns, urologic treatment can address issues like varicocele or blockages, supporting fertility and family planning.Enhance Cancer Outcomes:
In cases of urologic cancers, early surgical or medical treatment improves survival rates and reduces the risk of recurrence.Avoid Emergency Situations:
Delayed treatment may result in emergency situations like kidney obstruction, severe infections, or bladder retention requiring urgent care.
Invasive urology encompasses various surgical and interventional procedures:
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): Commonly performed for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) to alleviate urinary obstruction.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): Used for large or complex kidney stones.
Ureteroscopy: For diagnosing and treating conditions like strictures, stones, or tumors within the ureters.
Cystectomy: Partial or radical removal of the bladder, often due to cancer.
Prostatectomy: Surgical removal of the prostate gland, typically for prostate cancer.
Urethroplasty: Surgical repair of urethral strictures.
Stent Placement: Insertion of a stent to relieve obstructions or strictures.
Post-operative rehabilitation is essential for recovery and optimal outcomes:
Physical Therapy: Pelvic floor exercises to improve bladder control and reduce incontinence.
Pain Management: Use of medications and techniques to manage post-surgical pain.
Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary changes, fluid management, and smoking cessation to support healing.
Regular Monitoring: Follow-up appointments to assess recovery and detect any complications early.
Preventive strategies aim to reduce the risk of urological conditions requiring invasive interventions:
Hydration: Adequate fluid intake to prevent urinary tract infections and stone formation.
Dietary Modifications: Reducing salt and oxalate-rich foods to prevent kidney stones.
Regular Screenings: Especially for individuals with a family history of urological cancers.
Safe Sexual Practices: To prevent sexually transmitted infections leading to urethral strictures.
Avoidance of Irritants: Limiting exposure to substances that can irritate the urinary tract.
Timely Medical Consultation: Seeking medical advice for persistent urinary symptoms to prevent progression to invasive conditions.
WHY US?
Why Choose Dr. Ankit Gupta
At our clinic, Dr. Ankit Gupta offers expert care in urology, kidney transplantation, and andrology. With extensive experience in reconstructive and microscopic urology, as well as proficiency in laparoscopic and robotic surgeries, Dr. Gupta employs advanced techniques to ensure optimal outcomes and smoother recoveries for his patients.
70,000+
Patients Experience
10,000+
endoscopic surgeries
1000+
Urologic Oncologist surgeries
1000+
Invasive Urology Surgeries
Check Surgery Cost
We believe in transparency. You can enquire about the Surgery Cost and we will help you with complete detailed treatment process till your recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Invasive urology involves procedures and surgeries used to diagnose or treat conditions of the urinary tract and male reproductive system, often requiring entry into the body through instruments or surgery.
Common conditions include kidney stones, bladder tumors, enlarged prostate (BPH), urinary obstruction, and urologic cancers such as prostate or bladder cancer.
No. It includes both minimally invasive (like endoscopy, laparoscopy) and major open surgeries, depending on the condition and severity.
Techniques like ureteroscopy, laser lithotripsy, TURP, or robotic-assisted surgery involve small incisions or natural openings, reducing pain and recovery time.
They are generally safe and effective when performed by a trained urologist. Like any procedure, there are risks, but serious complications are rare.
Some procedures are outpatient, while others may require a short hospital stay, especially if general anesthesia or extensive surgery is involved.
Recovery depends on the procedure type. Minimally invasive methods often allow return to normal activities within a few days, while major surgery may take weeks.
Many procedures offer long-term relief or cure, especially for stones, obstruction, and localized cancers. However, some conditions may need ongoing monitoring or treatment.
What Our Patients Sayy
Based on 160 reviews








My experience with Dr. Ankit Gupta was very good. He treated my left kidney stone with laser surgery. I was discharged the next day after the surgery. He is the best urologist and kidney stone doctor in Gurgaon. 🙏
Best Regards
Subodh Rathore

